
Warehouse management is all activities related to receiving, storing, preserving, arranging, inventorying and exporting goods in the warehouse of an enterprise. It includes from when goods are imported to the warehouse, stored, moved in the warehouse, when there is an order, picking goods, packing and exporting goods, until returning or periodic inventory.
Effective warehouse management requires coordination between people, processes, equipment as well as information systems to ensure goods are of the right quality, quantity, location and time.

Warehouse management process is not only about arranging goods but also a key factor that directly affects the cost, performance and competitiveness of the enterprise. Below are the outstanding benefits that an effective warehouse management system brings.
Optimize storage costs: When goods are stored for too long, the enterprise has to bear additional costs of space, storage and capital. Good warehouse management helps shorten storage time, reduce inventory, thereby significantly saving operating costs.
Increase order fulfillment: Goods are scientifically arranged and easy to access, helping employees quickly find and export goods. This ensures delivery progress, improving customer experience and satisfaction.
Reduce the risk of damage, expiration or loss: A tight warehouse control system helps businesses track the status of goods by batch, by expiry date, avoid long-term inventory, minimize unnecessary loss and damage.
Improve transparency and inventory efficiency: Clear warehouse data helps businesses accurately grasp the quantity and location of inventory, thereby making timely and accurate decisions on importing - exporting or transferring goods.
Support supply chain and logistics operations: Warehouses are an important link in the supply chain. When the warehouse management process is optimized, the activities of importing, transporting and distributing goods become synchronized, helping to improve the efficiency of the entire logistics system.

In warehouse management activities, arranging goods properly plays a key role in helping businesses optimize storage space, improve work efficiency and limit errors in the import and export process. To achieve that, warehouse managers need to apply scientific principles, ensuring systematicity and suitability to product characteristics. Below are three of the most common and effective principles in arranging goods in the warehouse.
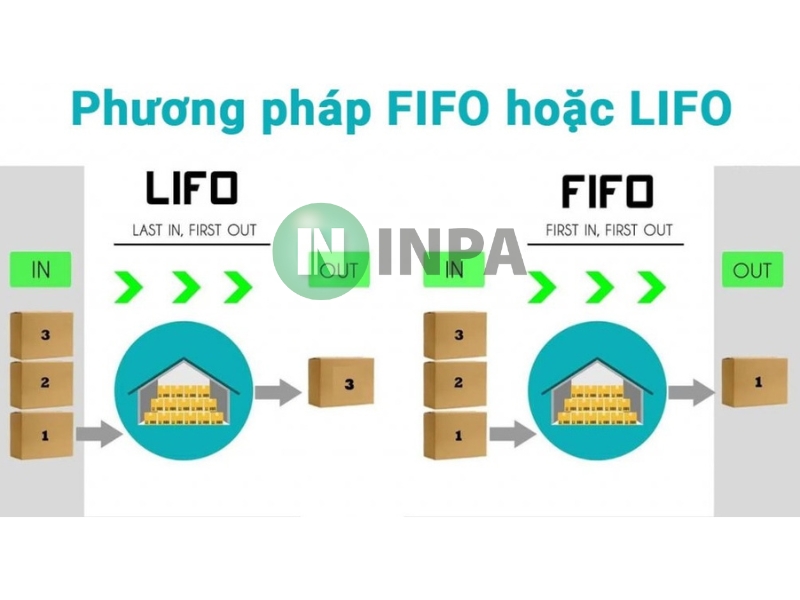
The three principles of FIFO, LIFO and FEFO are the foundation of goods circulation management. Specifically:
FIFO (First In - First Out) means that goods imported first are exported first. This principle helps avoid long-term inventory, especially useful for goods with limited shelf life or perishable goods.
LIFO (Last In – First Out) on the other hand, the last imported goods are exported first, often applied to items with a short life cycle or rapid changes in design and technology.
FEFO (First Expired – First Out) prioritizes exporting goods with the nearest expiry date, suitable for the food, pharmaceutical or cosmetic industries.
Choosing the appropriate principle helps businesses control product quality, minimize the risk of damage, and maintain a stable flow of goods in the warehouse.
SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) is a unique identification code for each type of product, based on characteristics such as size, color, style or supplier. Arranging warehouse by SKU makes searching, inventory and inventory management faster and more accurate. Each SKU is assigned a fixed location in the warehouse, which can be marked with a barcode or QR code to support automation. This arrangement is especially effective for businesses with a rich product catalog, avoiding confusion between similar products and helping to optimize import and export processes.

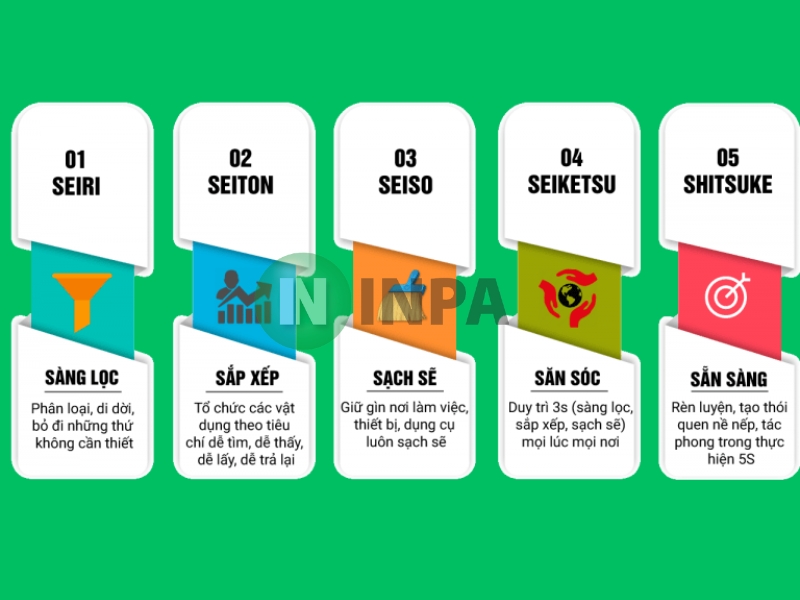
The 5S standard originates from Japan, including: Seiri (Sort), Seiton (Sort), Seiso (Clean), Seiketsu (Standardize) and Shitsuke (Readiness). Applying 5S in warehouse arrangement helps create a neat, scientific and safe working environment.
Sort: Remove unnecessary items and goods.
Arrange: Arrange goods in order, easy to find - easy to take - easy to return.
Clean: Keep the storage area clean, reduce the risk of damage to goods.
Care: Maintain the 5S process regularly.
Readiness: Form a habit of complying with regulations in all warehouse activities.
Thanks to applying 5S, businesses not only optimize the area and working time but also improve the spirit and sense of responsibility of warehouse staff.
A warehouse management process is not just a series of technical operations, but a foundation to help businesses control resources well, optimize costs and improve operational efficiency. When built and operated properly, this process brings many practical values, directly affecting business efficiency and customer experience.
Better preservation of goods: Receiving, storing and exporting goods according to standard processes helps goods to be preserved in suitable conditions, minimizing the risk of damage, loss or expiration. Thanks to that, businesses significantly reduce costs arising from defective goods, returned goods or inventory handling costs. A scientifically managed warehouse also helps to easily trace the origin, improve transparency and professionalism in operations.
Improve sales efficiency: When goods are clearly arranged, the system is accurately located and the picking process is fast, the operating team can process orders more accurately and promptly. This not only saves time and manpower but also increases customer satisfaction - a key factor in strengthening brand reputation and promoting sustainable revenue.
Avoid overstocking or understocking: An effective warehouse management system allows businesses to closely monitor actual inventory quantities, import - export speeds and consumption trends. Thanks to that, businesses can come up with a reasonable import plan, avoid overstocking causing waste of storage costs, or shortages that disrupt the supply chain. This balance helps stabilize cash flow and optimize overall business performance.

Warehouse management is a key step in logistics operations, ensuring that goods are stored, controlled and circulated effectively. A systematic warehouse management process not only helps businesses minimize losses and save costs, but also improves operational productivity. Below are the basic steps in the warehouse management process.
Warehousing is the first stage in the warehouse management process, when goods are received from suppliers or production departments. Warehouse staff will check the quantity, type, and quality of goods against the delivery documents to ensure accuracy. After checking, the goods are labeled, updated into the management system, and arranged in the appropriate storage location.
Warehousing is the process of preserving goods in the warehouse to maintain quality and be ready for the next activities. Warehousing work must comply with regulations on storage conditions (temperature, humidity, fire safety, etc.). At the same time, goods are arranged scientifically according to the principles of easy to find, easy to take, and easy to control, helping to optimize storage space and reduce operating time.
When there is a request from the sales or production department, the warehouse staff will pick up the goods according to the delivery note or delivery order. This process requires high accuracy to avoid errors in selecting the wrong product, quantity or batch. The application of barcodes, QR codes or warehouse management systems (WMS) helps to improve efficiency and limit confusion in this stage.
Warehouse output is the step where goods are taken out of the warehouse to be transferred to customers, agents or other departments. Warehouse staff must carefully check the order information, create warehouse output documents and record them in the system. Strict control of the warehouse output stage helps to avoid loss and support accounting and statistics work later.
Returns occur when goods are returned due to errors, damage, incorrect specifications or remaining after delivery. This process includes receiving returned goods, checking the condition, classifying goods that can be reused or need to be discarded. All information must be fully updated to ensure transparency and accuracy in the warehouse books.
Inventory is an activity performed periodically to compare actual data with data on the system. Inventory helps to promptly detect discrepancies, loss or damage to goods, thereby having appropriate remedial measures. This is also an important basis for financial reports and warehouse management decisions.
The final step in the process is to synthesize and analyze warehouse data to create statistical reports. The report includes the import - export - inventory situation, goods turnover rate, near-expiry or slow-moving goods. This information helps the management board evaluate the efficiency of warehouse operations, plan supply and adjust reasonable inventory strategies.
In the era of Industry 4.0, warehouse management is undergoing a strong revolution thanks to the application of advanced technologies. Modern solutions such as autonomous vehicles, automated warehouse systems or collaborative robots not only help optimize operating processes but also improve efficiency, reduce errors and labor costs. Below are three typical technologies that are widely deployed in smart warehouses today.
AGV is an automated goods transport device, capable of moving in a warehouse without a direct operator. They are guided by technologies such as laser sensors, magnetic fields, or virtual positioning maps (SLAM), helping the vehicle determine the exact location and safe travel route.
Automating internal transportation: Helps reduce the time it takes to move goods between storage and production areas.
Increasing accuracy and safety: Thanks to sensors and intelligent navigation systems, the vehicle can avoid collisions and operate stably in complex environments.
Reducing labor costs: AGV can work continuously 24/7 without rest, helping to save costs in the long term.
b. Practical application
AGV is often used to transport pallets, boxes, raw materials in warehouses, distribution centers or factories of large corporations such as Amazon, Samsung, and Vinamilk.
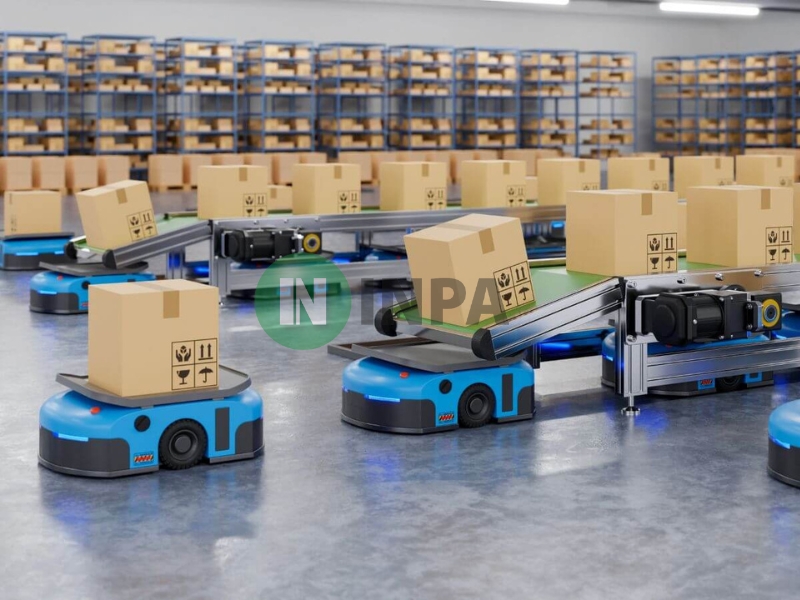

AS/RS warehouse system, also known as smart warehouse shelves, is a fully automated storage and retrieval system that uses robots or mechanical devices to move goods into or out of storage locations in the warehouse. This system is integrated with warehouse management software (WMS) to track, locate and coordinate activities accurately down to each unit of goods.
Optimizing storage space: AS/RS can arrange goods according to height and high density, making the most of warehouse space.
Fast and accurate processing speed: The automatic system helps minimize errors in importing and exporting goods, while shortening operation time.
Real-time data connection: Helps managers track the status of goods, storage locations and inventory status instantly.
AS/RS is used in modern logistics centers, warehouses of automobile, electronics and e-commerce manufacturing enterprises, where high speed and accuracy are required.

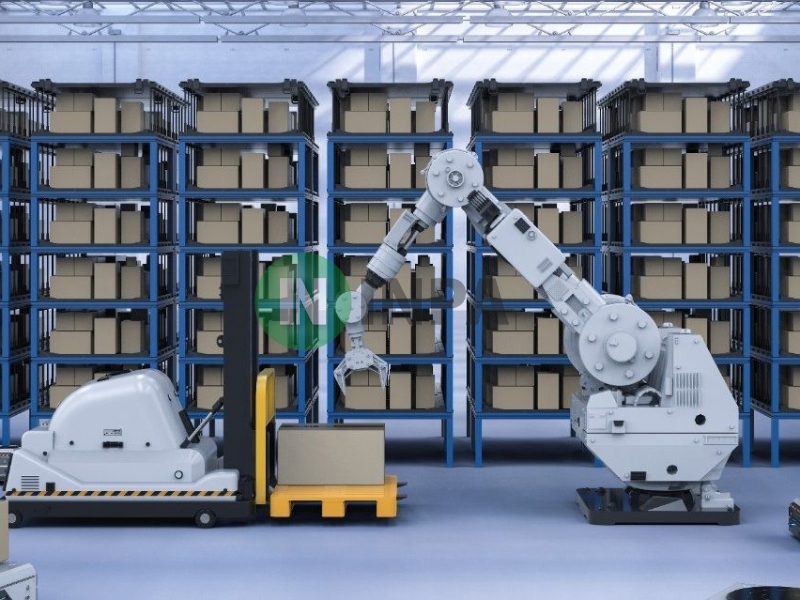
Collaborative robots, or Cobots, are a generation of robots that can work with humans in the same space without protective barriers. They are designed to support repetitive, heavy tasks or tasks that pose a risk of injury to workers.
Increased efficiency and productivity: Cobots can work continuously, supporting humans in stages such as packaging, loading, checking goods, labeling, etc.
Flexible and easy to program: Thanks to sensor technology and artificial intelligence, robots can quickly adapt to new processes or products.
Safety when interacting: Cobots are equipped with force sensors that help detect and stop operation when there is unexpected contact, ensuring human safety.
In warehouses of companies such as DHL or Shopee Xpress, cobots are deployed to work with employees in sorting and packaging, helping to double productivity while ensuring flexibility in operation.

A warehouse management process is not simply about storing goods but a strategic process - from warehousing, storing, retrieving, exporting, returning goods to inventory and reporting. When businesses apply the correct arrangement principles (such as FIFO, LIFO, FEFO), arrange by SKU, according to 5S standards, combined with clear processes, they will achieve high efficiency in warehouse operations. At the same time, taking advantage of 4.0 warehouse management technologies such as AGV, AS/RS, collaborative robots will help businesses increase competitiveness, reduce costs, increase flexibility and better meet the changing needs of the market. Therefore, for any business, large or small, building and maintaining a professional, modern warehouse management system is a worthy investment for sustainable development.
